Haptivity®
Haptivity® is Kyocera’s virtual reality technology that allows the simulation of a mechanical knob and further haptic effects on any surface.
Markets
Automotive
The automotive market is asking for haptic solutions for about 2 to 3 years.
The operation of automotive T/Ps without haptic feedback does not offer a „fool proof“ operation and is consequently distracting the driver as the input has to be verified with different senses.
The automotive industry would like to make the overall interior smoother and more homogeneous – and consequently replace mechanical switches but would like to keep the haptic feedback of those switches the driver is used to.
So far, haptic feedback systems used in the automotive market are all based on magnetic solutions – with respective drawbacks like constructions space, slow response and limited functionality.
Industrial
The industrial HMI market is asking for haptic solutions for about 2 to 3 years, similar to the automotive HMI market.
Currently, for the industrial market there is no solution under mass production.
Haptics are not only requested for use cases with the incorporation of a display, but also for the replacement of singular mechanical switches or even complete keyboards.
The implementation of haptics into industrial displays is challenging since there are specific requirements regarding dust- and waterproofness.
Outstanding Features of Kyocera’s Haptivity® Technology
- Simulation of a mechanical button on any surface (touchpad / touchscreen).
- Actuators are multilayer piezos with very small construction space requirements (60 mm x 10 mm x 10 mm). In certain configurations the actuators can also be used as pressure sensors.
- The actual mechanical movement of the touch surface is 50-80µm.
- Haptic parameters of the simulated button (the subjectively perceived „click“) are controlled by S/W and are widely adjustable only by S/W.
- Various design elements as sliders or rotators can be realized.
- The technology is covered by more than 100 Kyocera patents.
Scheme of a Multi-Layer Piezo
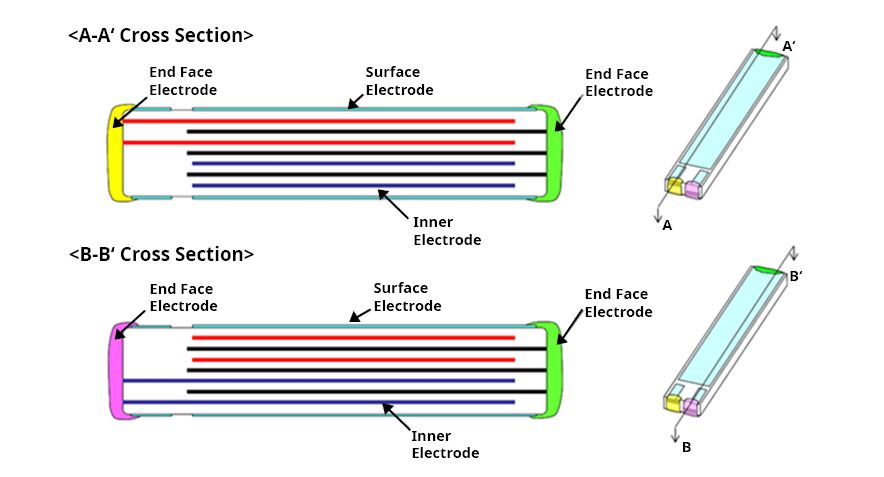
- The number of layer lamination is shown as "8 layers," which is a typical example.
- Common structure for uni-morph and bi-morph, therefore A-A' and B-B' are different.
Haptivity® Principle
In order to simulate a mechanical button it is not sufficient to apply just a vibration to the surface that has been touched from the operator. It is absolutely essential to generate a distinctive surface vibration only after the operator has exceeded a certain pressure threshold – similar to a mechanical button.
Therefore, the device must comprise a component that is able to measure the applied pressure. In certain configurations this can be the actuator piezo itself (by utilizing the reverse piezo-electric effect of the actuator functionality), but in general it should be a separate pressure sensing component.
After a pressure threshold has been exceeded (which is detected from the implemented controller), a single sine half wave of ~30 V is applied to the actuator piezos. According to the piezo-electric effect, the piezo(s) change the geometry. With a suitable mechanical device this piezo shrinkage is converted into a lateral movement which is coupled into the touch surface.
How to Implement Haptivity® into your Device?
Key Points
- An efficient mechanical implementation of the piezo actuator(s) into the HMI.
- A proper electrical driving of the piezo actuator.
Mechanical Integration
The actuator / booster block (schematically illustrated below, length about 6 cm) has to be attached tightly onto the device which has to be vibrated - ideally on the rear side- by screwing or gluing. The mounting position does not necessarily have to be centered at the device.
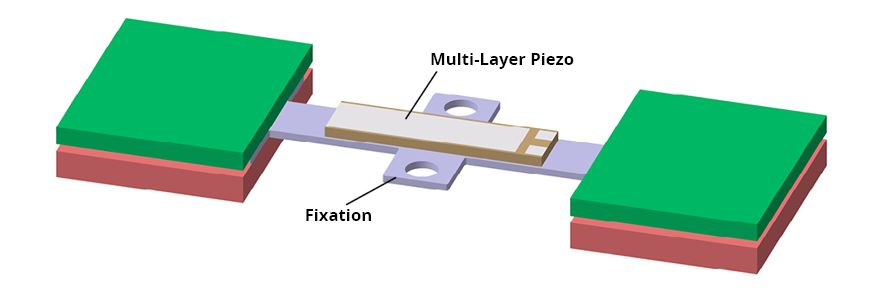
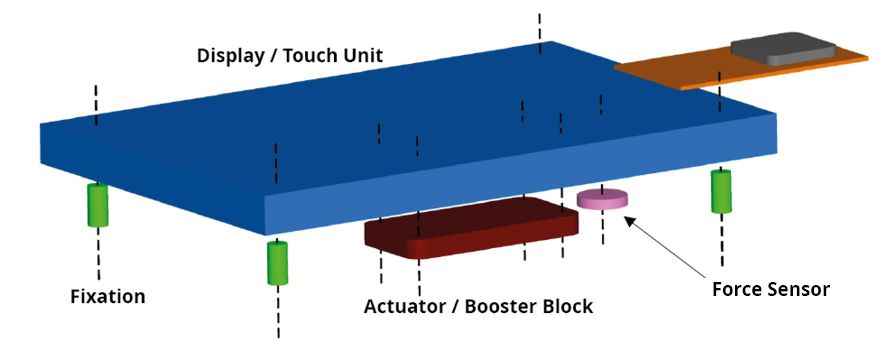
Below illustration shows the general design of a device with implemented Haptivity®
To make the generation of the driving scheme as convenient as possible and adoptable to customer needs, a building block - like electronical architecture is provided.
The main components are an amplifier with integrated DC/DC converter and an applications processor (PSoC). They are accompanied by peripheral components as the touch and the pressure sensor.
Large volume applications
The driving components are typically implemented onto the customer’s board:
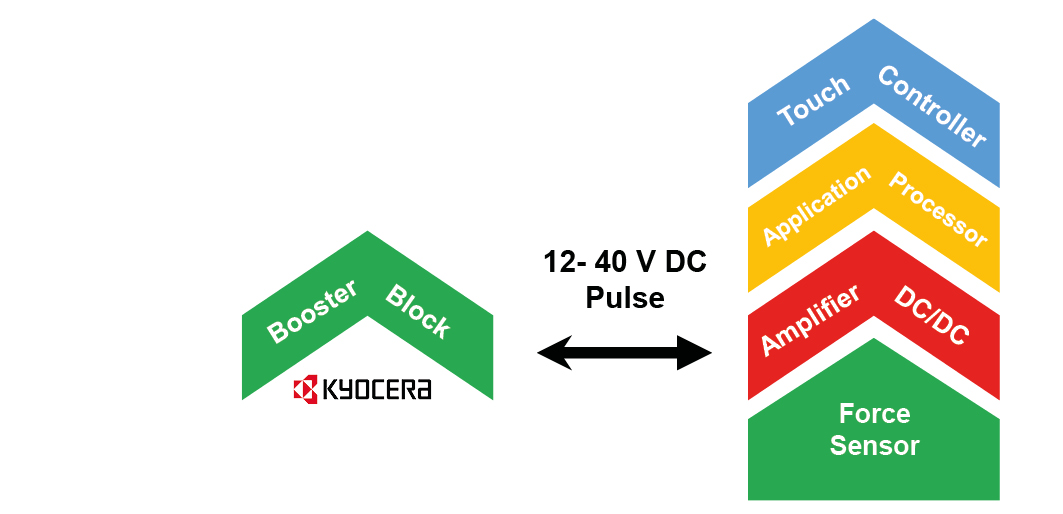
Small volume applications
The driving components can be provided from Kyocera along with the booster-actuator:
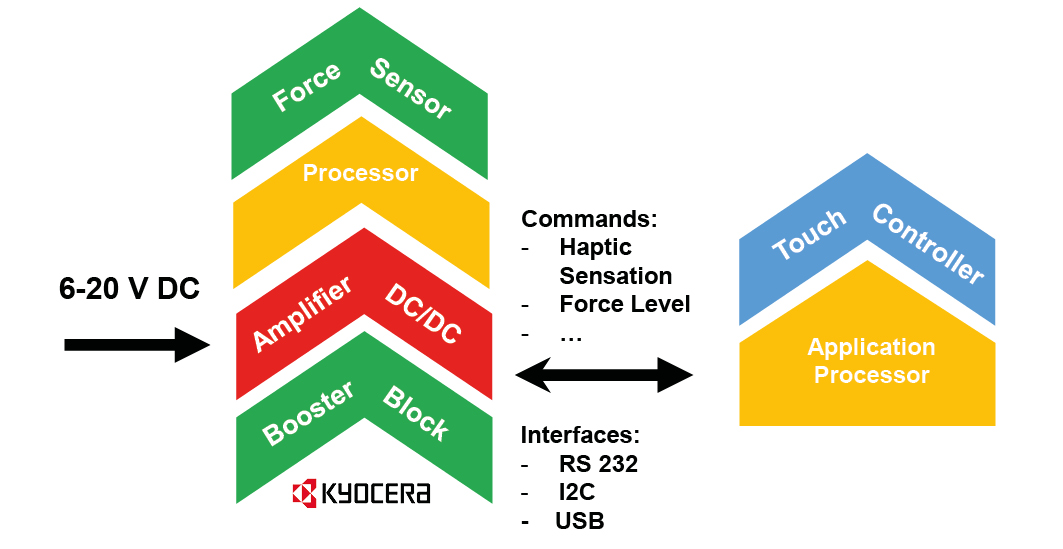
This simplifies the control of the haptic event to a standard serial communication from the customer’s ECU to the Haptic unit.
Development Kit
For an individual investigation and testing, Kyocera provides a Development Kit, containing actuators as well as a complete driving system with different driving features.
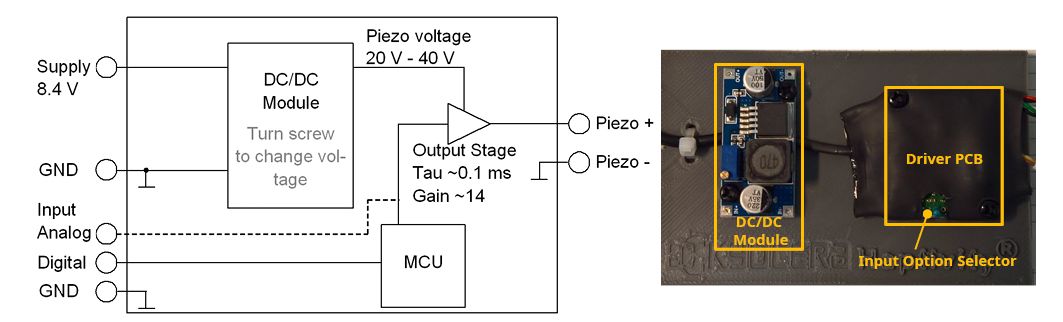
For details or an offer for the Development Kit, please call us or use the contact form on this page.

